Dr. Richardson and Dr. Memsic are two of the top breast surgeons in Los Angeles, using innovative techniques to create excellent clinical and aesthetic outcomes.
Schedule a Visit
Bedford Breast Center
436 N Bedford Dr, Ste 308
Beverly Hills, CA 90210
Phone: (310) 278-8590
Monday – Friday: 9 a.m.– 5 p.m.
3D Mammogram
Bedford Breast Center provides 3D mammograms in Beverly Hills for Los Angeles area women who want a better mammogram experience. Unlike traditional mammography, which takes one image of the breast, 3D mammography takes multiple images to create a three-dimensional picture. Additionally, the 3D system uses less compression and radiation than conventional digital 2D mammography.
What Is a Mammogram?
A mammogram is an X-ray image of the breast that shows changes in the tissue. It is the most effective method for breast cancer screening in the early stages. It is often the first line of early detection. Generally, mammography is divided into two categories: screening and diagnostic.
Routine screening mammography has long been the best way to catch breast cancer in the earliest stages when the disease is most treatable.
Why Do I Need a Mammogram?
Routine screening mammograms can detect the presence of cancerous cells before they grow or spread, which can significantly increase survivability. Mammograms can reveal breast lumps before they can be felt during a breast self-exam or clinical breast exam. They can also detect tiny clusters of calcium, which can be caused by cancer, fatty cells, or cysts. Additional breast screening methods may be needed to determine if abnormal cells are present.
Visit medlineplus.gov to learn more about the importance of routine mammograms.
“Always a great experience! Carmen takes the best, pain free, mammograms I ever had. They have the latest, state of the art machine! Everybody at Bedford Breast Center are amazing and they make you feel very comfortable. My highest recommendation!”
Maggie Z. – Yelp
What To Expect During a Mammogram
Before your mammogram, you’ll undress from the waist up. You’ll remove your top and bra and put on a gown (provided by the mammography medical center) in a changing room.
A nurse will take you to the mammography room, where our mammography technician will position your breast between two flat panels that gently compress the breast to flatten and spread out the tissue.
Once you are correctly positioned, the mammography technician will either leave the room or go behind a screen and begin taking the X-rays. This process of positioning and imaging is repeated for additional views and the other breast. Typically, 2 views are taken of each breast—4 if you have breast implants.
The entire process for a screening mammogram takes between 10 to 20 minutes for conventional mammography and 5 to 10 minutes for digital mammography. Diagnostic mammograms typically take longer because additional views and images are needed.
Preparing for a Mammogram at Bedford Breast Center
Here are some do’s and don’ts for a comfortable mammogram that goes as smoothly as possible:
Do’s:
- For better accuracy and comfort, schedule your mammogram for a day just after your period when breast tissue is least tender and has the least water retention.
- Advise the appointment scheduler if you have breast implants.
- Bring previous mammography films or images on a CD. Imaging centers cannot send them instantly, so bring them with you or notify your former center 1 to 2 weeks before the appointment.
- Wear separates (pants or a skirt and a top) so that you can keep your bottoms on during the exam. If you wear a dress, you may feel more exposed once you remove it. We provide a wrap, but most patients prefer to keep their skirts or pants on during the procedure.
- To reduce discomfort, take acetaminophen or ibuprofen on the morning of your mammogram and avoid salty food the day before.
- RELAX! Stress can cause tension and involuntary motion during the exam, leading to the need for repeat images.
Dont’s:
- Do not wear deodorant, powder, or creams under your arms, as the metallic particles in most deodorants can create unnecessary spots on the images.
- Avoid wearing bulky jewelry that will have to be removed during the mammogram.
- Don’t worry about the results or the possibility of further tests. Follow-up tests allow us to recheck and investigate further but don’t necessarily indicate cancer is present.




Do Mammograms Hurt?
The technician will adjust the platform height to reach you easily. The mammogram machine will compress your breast on the imaging platform to capture the clearest and most accurate image. The compression can cause discomfort and may be painful for some women.
This compression is necessary, however, to allow the machine to get a clear and complete picture of your breast tissue. Compression lasts only a few moments while the images are taken, then the mechanism is released.
We do everything we can to keep patients as comfortable as possible. If you experience pain, please let our technician know. They will help you adjust your position for a more comfortable experience.
What Can a Mammogram Detect?
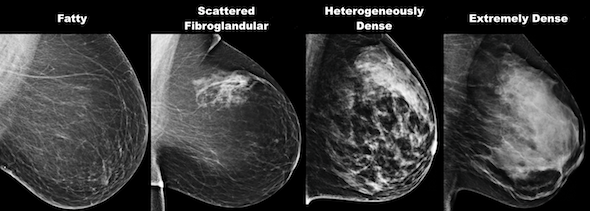
Mammograms can detect abnormalities in the breast that can be symptoms of cancer or other non-consequential irregularities:
- Cysts
- Lumps or masses
- Asymmetric areas on the mammogram
- Calcium deposits in ducts and other tissues (calcifications)
- Dense areas found in only one breast or one area of the breast
- An area that appears denser than on your last mammogram
- Fibroadenomas (movable, solid, rounded lumps made up of normal breast cells)
While looking for possible cancer, your doctors may identify masses or structures in the breast that deserve further investigation. A mammogram is the first in a series of breast screening tests that help reveal a more complete picture.
Contrast-Enhanced Mammography
Bedford Breast Center proudly offers contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM), an advanced imaging modality that provides more comprehensive results for patients who:
- Are currently undergoing breast cancer treatment
- Have higher breast cancer risk factors
- Received inconclusive or irregular imaging results
- Experience unexplained breast symptoms
- Have dense breast tissue
Why Choose Contrast-Enhanced Mammography?
- Superior Detection Capability: Iodine-based contrast dye highlights areas with increased blood flow, making potential cancerous lesions more visible against surrounding breast tissue.
- Enhanced Diagnostic Confidence: By combining structural imaging with functional blood flow information (similar to MRI), CEM provides complete diagnostic data in a single exam.
- Convenient Alternative to MRI: CEM delivers diagnostic benefits similar to breast MRI but uses standard mammography equipment, takes less time, and doesn’t require enclosure in a tight space.
Call Bedford Breast Center at (310) 278-8590 to learn more about contrast-enhanced mammography and if it’s appropriate for you.
Why Is a 3D Mammogram Better Than a Traditional 2D Mammogram?
A 3D mammogram can image multiple breast tissue segments in each pass. When viewed together, they recreate a 3D image of the breast.
- Traditional 2D mammography takes only one static image with each pass. A 3D mammogram gives our radiologist a more complete view of the breast. This improved clarity makes it easier to accurately diagnose breast cancer while reducing the chance of a false positive.
- With a 3D mammogram, our radiologist can see very small tumors that may be obscured on a 2D mammogram. This increases the likelihood that we will diagnose breast cancer in the earliest stages, which allows for the best possible treatment outcomes.
- Patients who have a 3D mammogram are less likely to be called back to the office for additional views, saving time, money, and the anxiety of repeat visits.
- 3D mammography is better at evaluating dense breast tissue than 2D mammography.
- Less compression and radiation exposure are required with 3D mammography.
Are Other Advanced Breast Imaging Options Available?
As a premier breast health center, we continually adopt the latest advancements in diagnostics to ensure you receive the most accurate and comfortable care. By incorporating cutting-edge technologies, we offer innovative imaging solutions such as the Koning Vera breast CT scan:
Koning Vera Breast CT Scan
The Koning Vera breast CT scan provides exceptionally detailed 3D images of your breast, allowing us to detect even the smallest lesions. If you have dense, small, or large breasts, breast implants, or tender breasts, the Koning Vera breast CT scan ensures a comfortable, no-compression experience.
What Is Digital Mammography?
Both conventional and digital mammography use X-rays to produce an image of the breast. Conventional mammography stores the image directly on film. Digital mammography is an electronic image stored as a computer file. The digital image can be enhanced, magnified, and manipulated for further evaluation much more easily than the film counterpart.
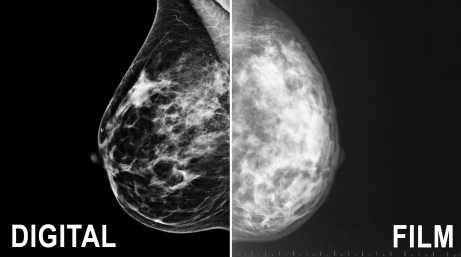
Digital mammography allows doctors to adjust, store, and retrieve digital images electronically, which offers several advantages over conventional mammography.
- Healthcare providers can share files electronically, making long-distance consultations, second opinions, and consultations with breast surgeons much easier.
- Subtle differences between normal and abnormal tissues may be easily examined.
- Fewer repeat images may be needed, reducing radiation exposure.
- Fewer follow-up procedures may be needed.
Digital mammography can be performed in facilities certified to practice conventional mammography. The procedure for having a digital or conventional mammogram is the same.
“This was my first time at the Bedford Breast Center. The office staff are amazing, so friendly and professional. The technician was great and and made my mammogram exam a pleasant experience. I highly recommend Bedford Breast Center and I will be returning annually. They deserve 10 stars!!”
Lolli W. – Google
Mammograms After Breast Cancer
If you have had surgery for breast cancer, such as a lumpectomy, mastectomy, or breast reconstruction after mastectomy, you’ll likely receive different recommendations for screening mammograms than women usually do.
Mammograms After Lumpectomy
If you had a lumpectomy and radiation therapy, you can expect to have a mammogram of the treated breast about 6 months after finishing treatment. Radiation can cause changes in the breast tissue and skin, so this 6-month mammogram will become the new “standard” against which future mammograms of the remaining breast tissue are compared.
Going forward, your doctor may say that yearly mammograms are sufficient or that the treated breast should still get a mammogram every 6 months for the next few years. Talk to your doctor about the plan that is best for you.
Mammograms After Mastectomy
If you have had a single breast mastectomy, no additional mammograms are needed on that side because the breast tissue has been removed. You will, however, continue with your yearly screening mammograms as usual on the remaining breast. Mammograms of the remaining breast are vital because having cancer in one breast raises your risk of developing cancer in the other. If you had a double mastectomy, you will no longer need mammograms since no breast tissue remains.


- No Compression - Comfortable, pain-free imaging
- Open Design - Won't trigger claustrophobia
- Ideal for Dense Breasts - Advanced detection with contrast
- Fast Results - Complete scan in under 10 minutes
Vera Scan with contrast provides enhanced detection comparable to MRI, delivering precise, accurate diagnosis in a fraction of the time.
Call (310) 278-8590 to reserve your appointment.
Is Vera Scan Right For You? Take The QuizMammograms After Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy
Mammograms will be recommended if you have had a nipple-sparing mastectomy or subcutaneous mastectomy. In this surgery, you keep your nipple and tissue under the skin. Enough breast tissue remains to warrant the continued use of screening mammograms.
Mammograms After Breast Reconstruction
In most cases, you will not need mammograms If you have had breast reconstruction after mastectomy. Regular physical exams of the reconstructed breast may be performed. Doctors may recommend mammography after breast reconstruction if:
- You’re at high risk for local recurrence
- Physical examination of the breast is difficult
- There is a questionable abnormality
Breast MRI is another and possibly more effective way to screen women who have had breast reconstruction and are at high risk for recurrence. Talk to your doctor about what they recommend for you, then contact Bedford Breast Center in Beverly Hills to receive the best screening mammogram Beverly Hills has to offer.
Mammogram FAQs
At what age should I start getting mammograms?
Age is only one factor to consider when determining when to start getting regular mammograms. If you are at low risk for breast cancer, your doctor will likely recommend getting mammograms every 2 years once you reach age 40. If you are high risk (have a family history of breast cancer or a history of precancerous breast lesions, for example), you may want to begin screenings sooner or more often.
What should women with breast implants do about screening mammograms?
Women with breast implants should continue to get screening mammograms. Let the facility know that you have them when you schedule your appointment. The technician and radiologist need to be aware of the presence of implants for the most accurate results possible. If you received implants following a mastectomy, ask your doctor whether a mammogram of the reconstructed breast is necessary.
“I went to Bedford Breast Center for my mammogram today. The Mammo Technologist Carmen was outstanding! She was very kind, professional and informative about the exam. I had a great experience and would recommend her to anyone. Terrific staff and facility all around.”
Allison G. – Google
Are there alternatives to mammograms?
Mammography is the go-to breast cancer screening technique, but there are other methods we can use. At Bedford Breast Center, 3D mammography is standard for all our patients to ensure we get the most accurate picture possible. Our doctors might use another imaging technique, such as an ultrasound or MRI, if we need to see other details after a mammogram. MRI may also be the best option if you have undergone reconstruction. Our doctors can recommend the best, least invasive option for you.
What are doctors looking for in a mammogram?
- Asymmetry between the breasts.
- Breast density: how fibrous and glandular tissues are distributed in your breast versus how much of your breast is fatty tissue.
- Calcifications or tiny mineral deposits, of which there are two kinds:
- Macrocalcifications: These large calcifications are not associated with cancer and are most likely due to changes caused by aging breast arteries, injuries, or inflammation. They are most common in women over 50.
- Microcalcifications: These are specks of calcium in the breast. The shape and layout of microcalcifications help the radiologist judge how likely cancer is present. In some cases, a biopsy might be needed to determine if it is cancerous.
- Masses caused by cysts or fibroadenomas:
- A simple cyst is made up of fluid and is rarely cancerous. A cyst and a tumor can feel alike on a physical exam and may look the same on a mammogram. We conduct a breast ultrasound to confirm that the mass is a cyst. Another option is a needle aspiration, which removes the cyst’s fluid with a thin, hollow needle.
- Fibroadenomas are movable, solid, rounded lumps made up of normal breast cells. These are the most common kinds of breast mass, especially in young women.
- Masses requiring further investigation.
How much radiation exposure do you get during a mammogram?
The radiation exposure experienced during a mammogram is lower than that experienced during a round trip flight from NYC to London, or even less than the radiation encountered in our everyday lives in the US over a 3-month period.
Our world-class facility serves patients from Beverly Hills, Los Angeles, Santa Monica, Glendale, Malibu, and beyond. To learn more or to schedule a mammogram, call us at (310) 278-8590 or contact us using the online form to schedule an appointment.